Hip Knee and Shoulder Specialist In Nashik. Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already decided to undergo hip replacement surgery, this information will help you understand the benefits and limitations of total hip replacement. This article describes how a normal hip works, the causes of hip pain, what to expect from hip replacement surgery, and what exercises and activities will help restore your mobility and strength, and enable you to return to everyday activities.
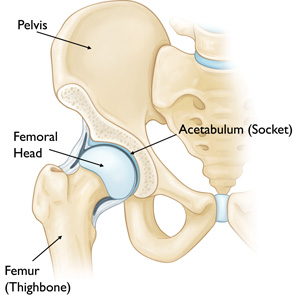
If your hip has been damaged by arthritis, a fracture, or other conditions, common activities such as walking or getting in and out of a chair may be painful and difficult. Your hip may be stiff, and it may be hard to put on your shoes and socks. You may even feel uncomfortable while resting.
If medications, changes in your everyday activities, and the use of walking supports do not adequately help your symptoms, you may consider hip replacement surgery. Hip replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure that can relieve your pain, increase motion, and help you get back to enjoying normal, everyday activities. Hip Knee and Shoulder Specialist In Nashik.